Abducens nerve
Last edit by Alaric Steinmetz on
The abducens nerve is the sixth cranial nerve and carries somatomotor fibers. It is responsible for the movement of the eyeball along with the oculomotor nerve and the trochlear nerve.
Anatomy
Innervation
The abducens nerve innervates the lateral rectus muscle and impairment of the abducens nerve leads to double vision.
Nuclei
The fibers of the abducens nerve originate from the nucleus of the abducens nerve, which is located in the pons at the floor of the fourth ventricle.
Course
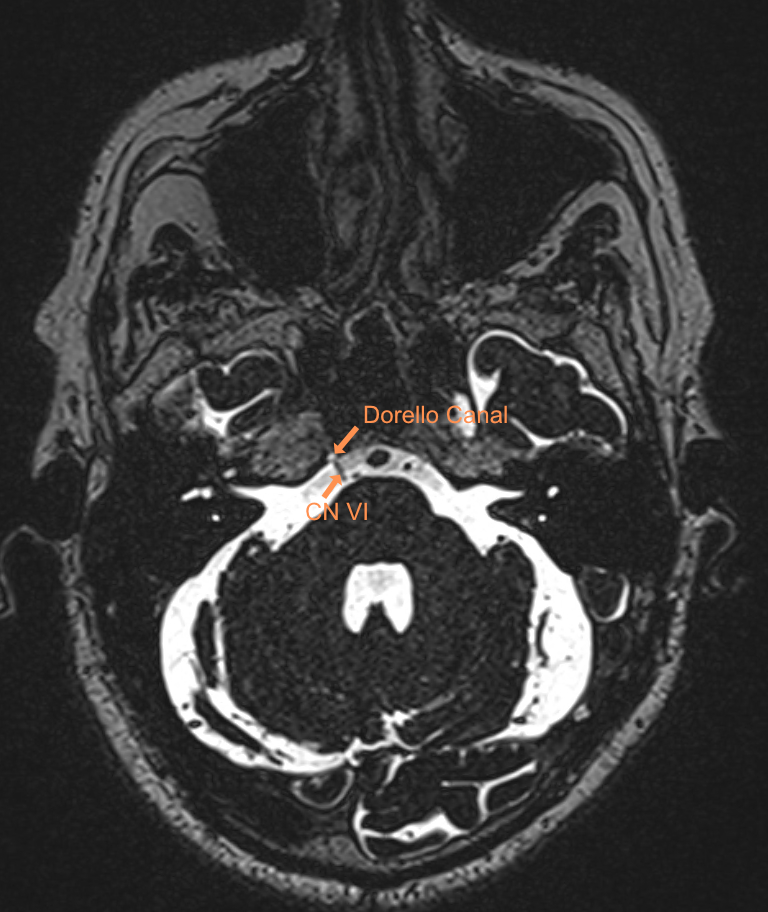
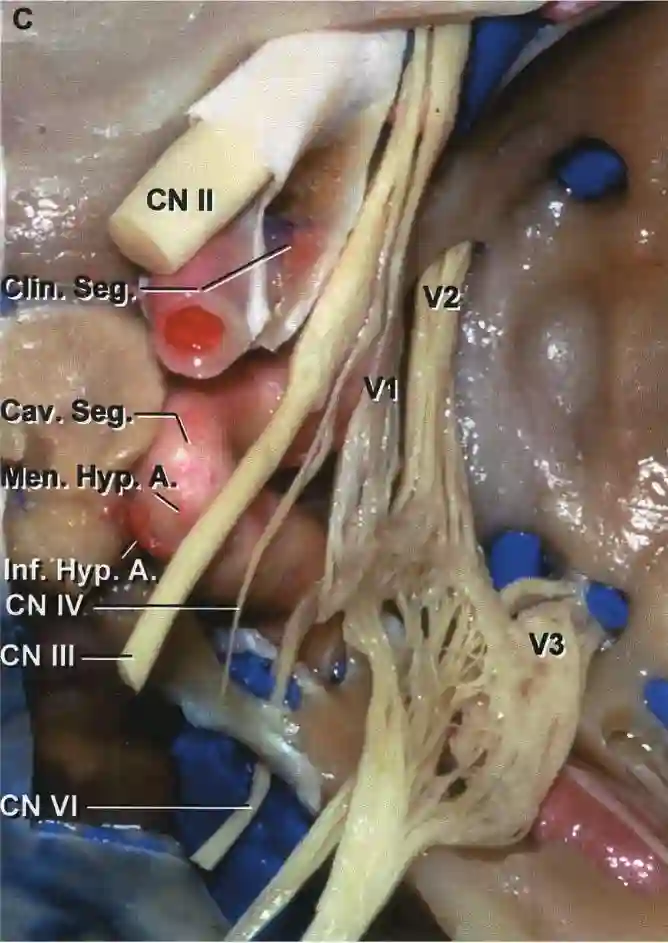
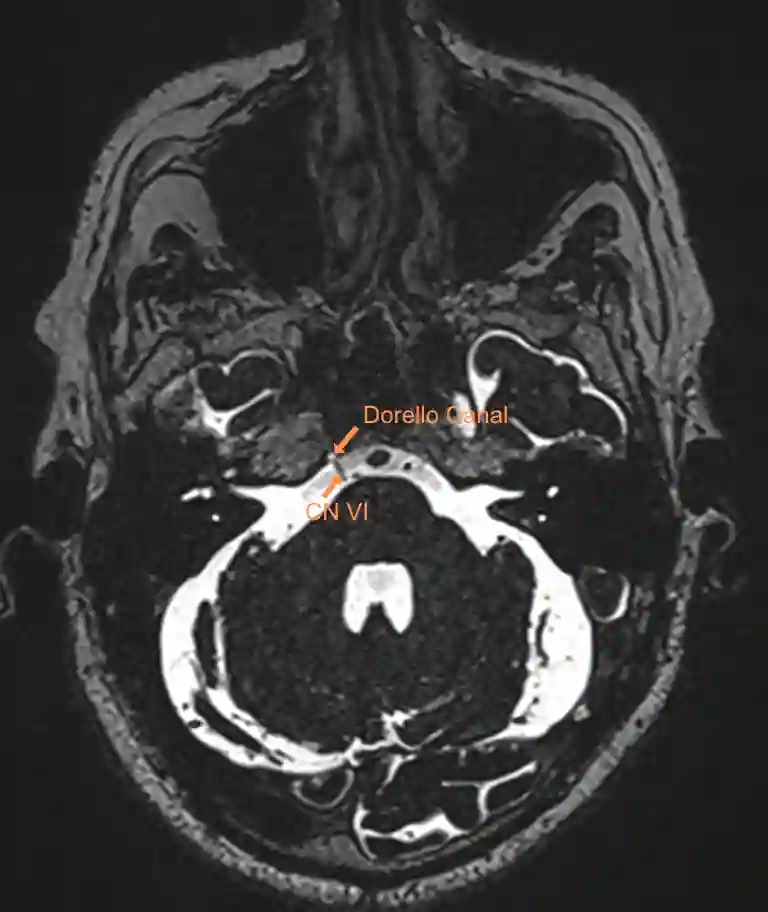
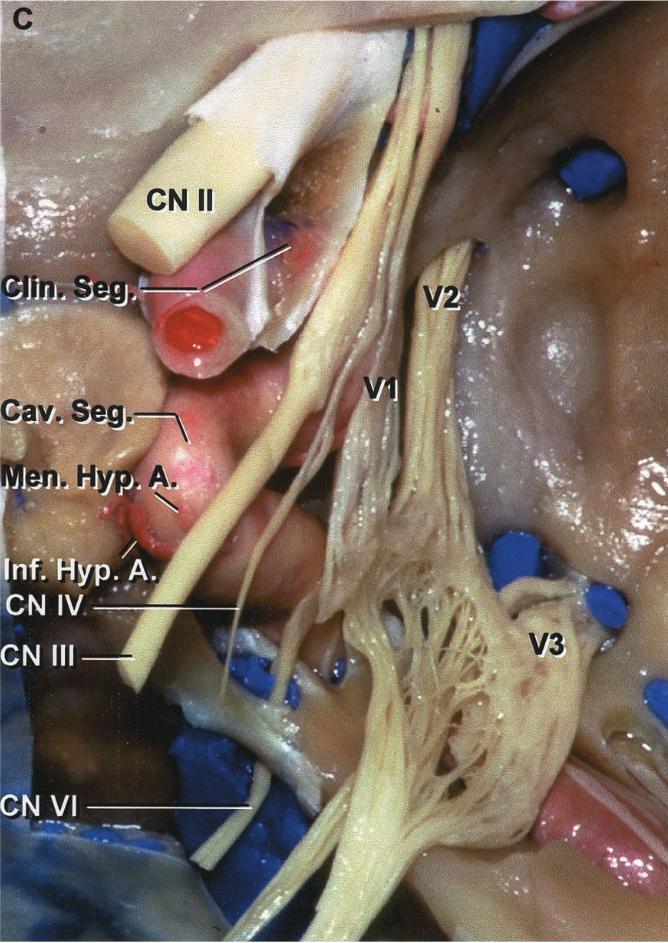
The abducens nerve originates at the brainstem at the junction between the pons and the medulla oblongata. It passes through the Dorello's canal into the cavernous sinus. Within the cavernous sinus, the abducens nerve is the only cranial nerve that runs freely in the sinus and is not located in the wall of the cavernous sinus. Subsequently, the abducens nerve passes through the superior orbital fissure into the orbit.
Illustration
Imaging