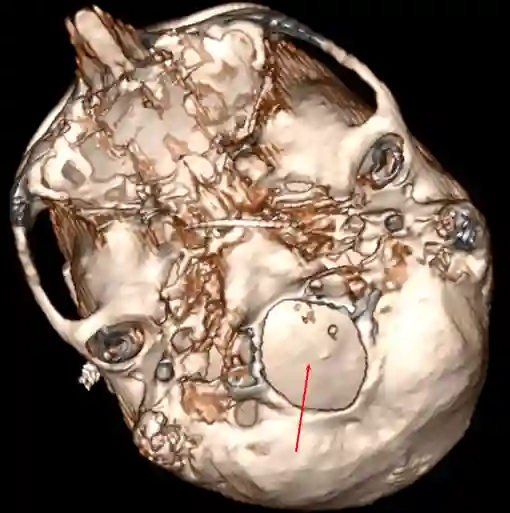
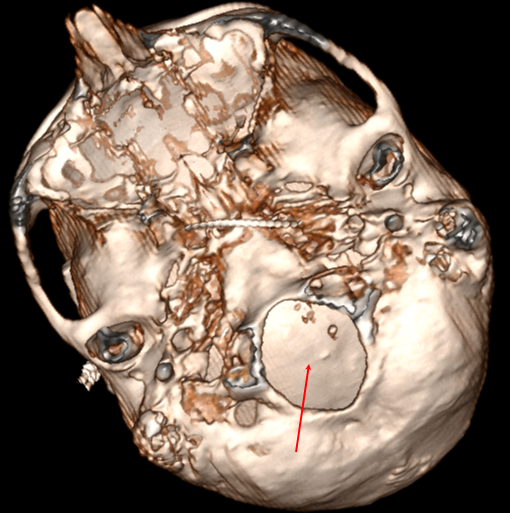
Foramen magnum
Last edit by Alaric Steinmetz on
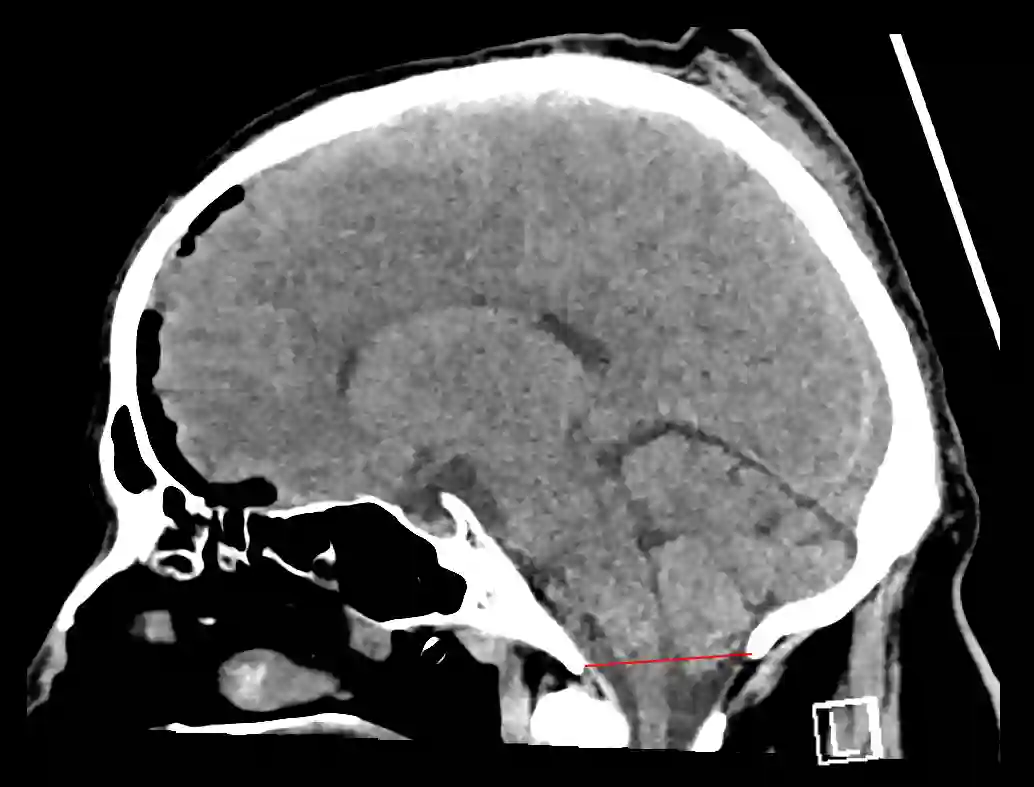
The foramen magnum is a bony opening in the region of the posterior cranial fossa, through which the medulla oblongata passes and thereby connects with the spinal cord.
Anatomy
The foramen magnum is located in the occipital bone. Alongside the medulla oblongata, the following structures pass through the foramen magnum:
Spinal root of the accessory nerve
The left and right vertebral artery
The right and left posterior spinal artery
Spinal vein
The foramen magnum marks the transition area of the cranial dura mater into the spinal dura mater.
Osteometric Measurement
The foramen magnum has the following sagittal and transverse osteometric dimensions[^1]:
Dimensions of the Foramen Magnum | Average | Minimum - Maximum |
Sagittal Diameter | 36.6 mm | 30.1 - 42.6 mm |
Transverse Diameter | 31.1 mm | 25.0 - 38.9 mm |
Imaging

Clinical Relevance
Herniation
In cases of excessively high intracranial pressure, parts of the brain can be displaced downwards into the foramen magnum, leading to a herniation.
Foramen Magnum Stenosis
In patients with a skeletal dysplasia, such as achondroplasia, stenosis of the foramen magnum can occur[^2].