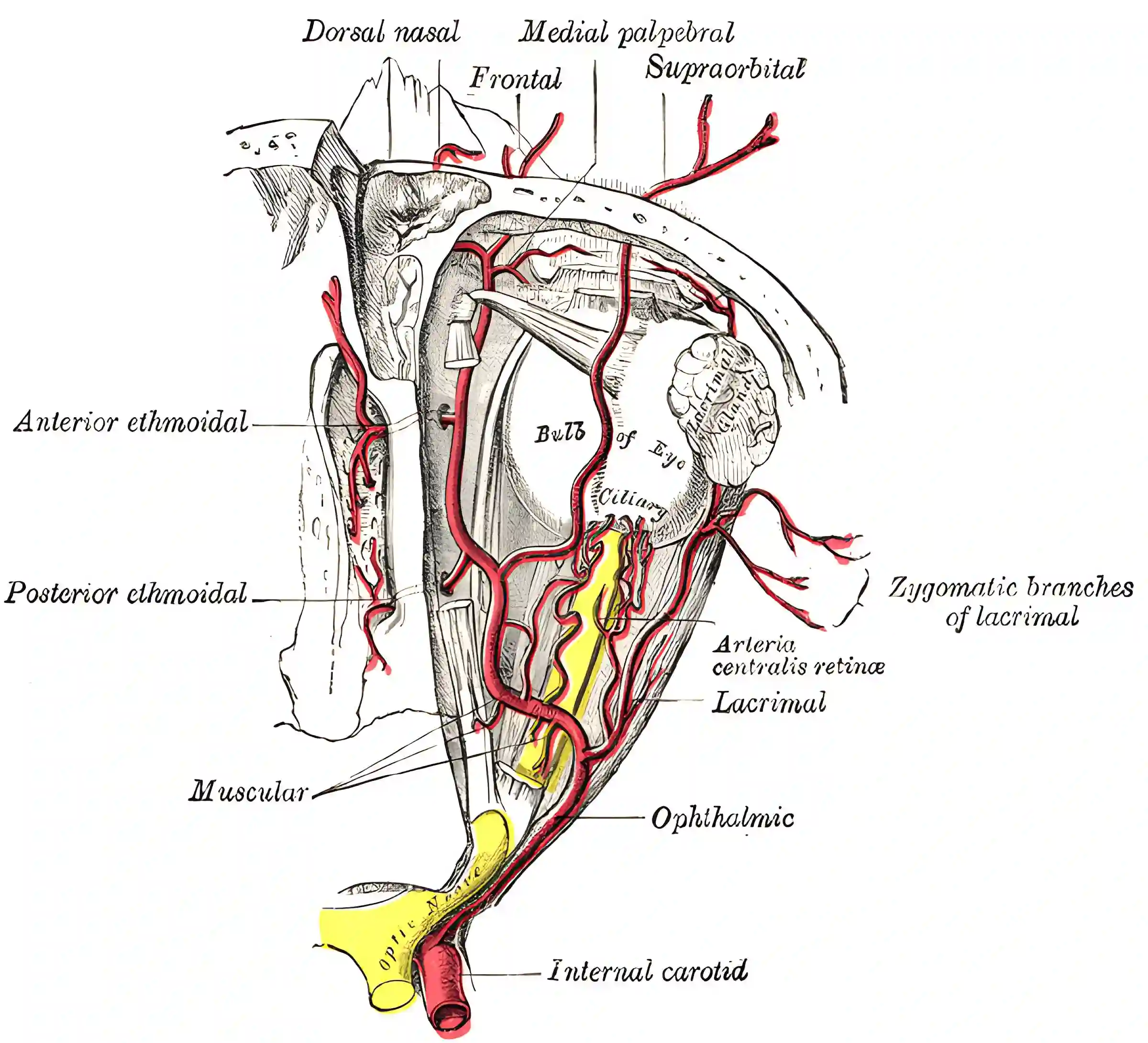
Ophthalmic artery
Last edit by Alaric Steinmetz on
Synonyms: Augenschlagader, ophthalmic artery
The ophthalmic artery arises as the first intracranial vessel branch from the internal carotid artery (ICA) before the posterior communicating artery.
Anatomy
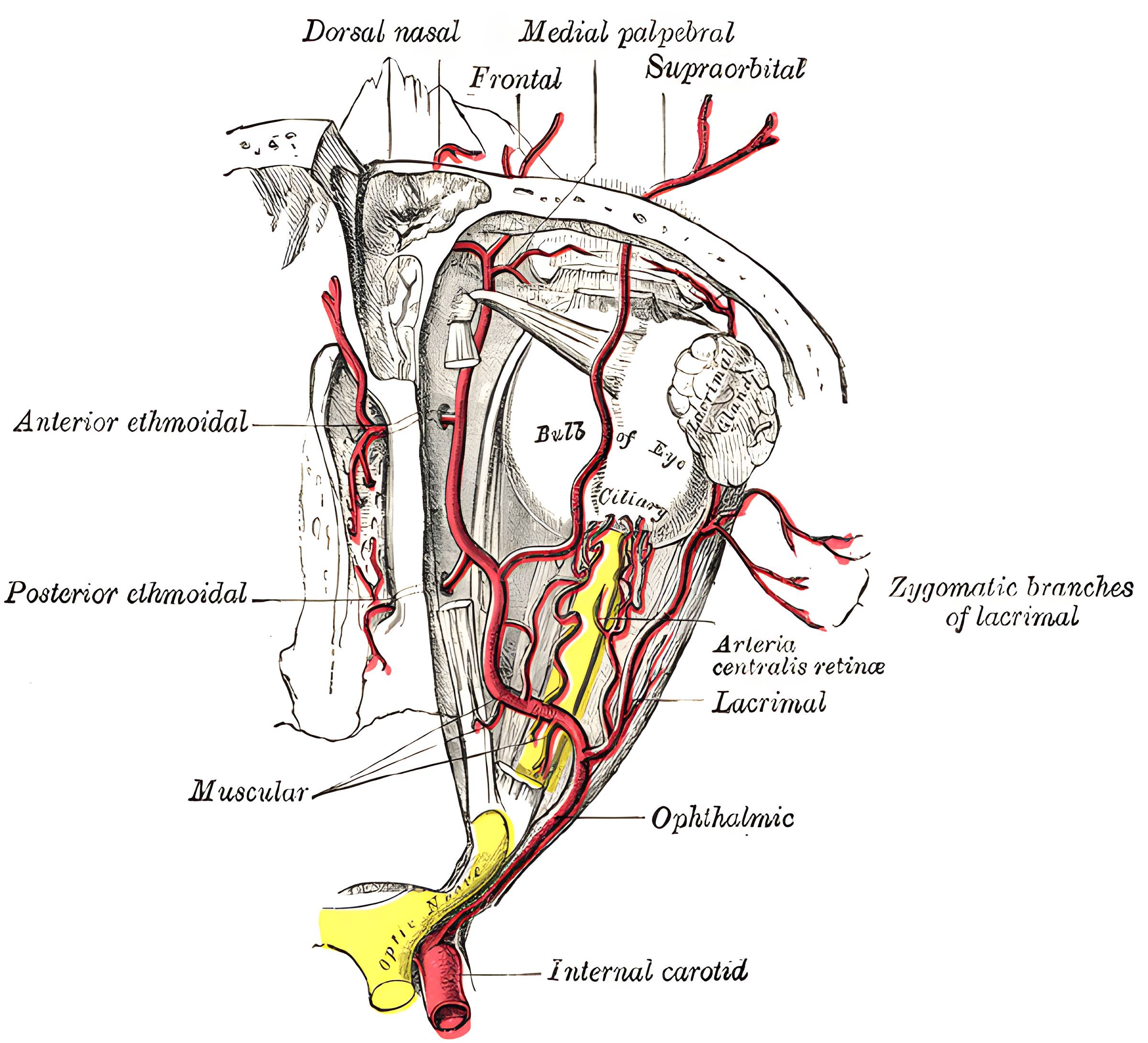
The ophthalmic artery courses inferior to the optic nerve through the optic canal into the orbit[^3]. The most important arterial anastomosis between the internal carotid artery and external carotid artery runs through the ophthalmic artery[^2].
Vascular Branches
The ophthalmic artery gives off the following arterial branches:
Central retinal artery
Long posterior ciliary arteries
Short posterior ciliary arteries
Muscular branches
Palpebral arteries
Dorsal nasal artery
Anatomical Variants
In approximately 89% of cases, the ophthalmic artery arises distal to the cavernous sinus, in about 8% of cases within the cavernous sinus, and in about 3% of cases, the ophthalmic artery is completely absent [^1].
Illustration
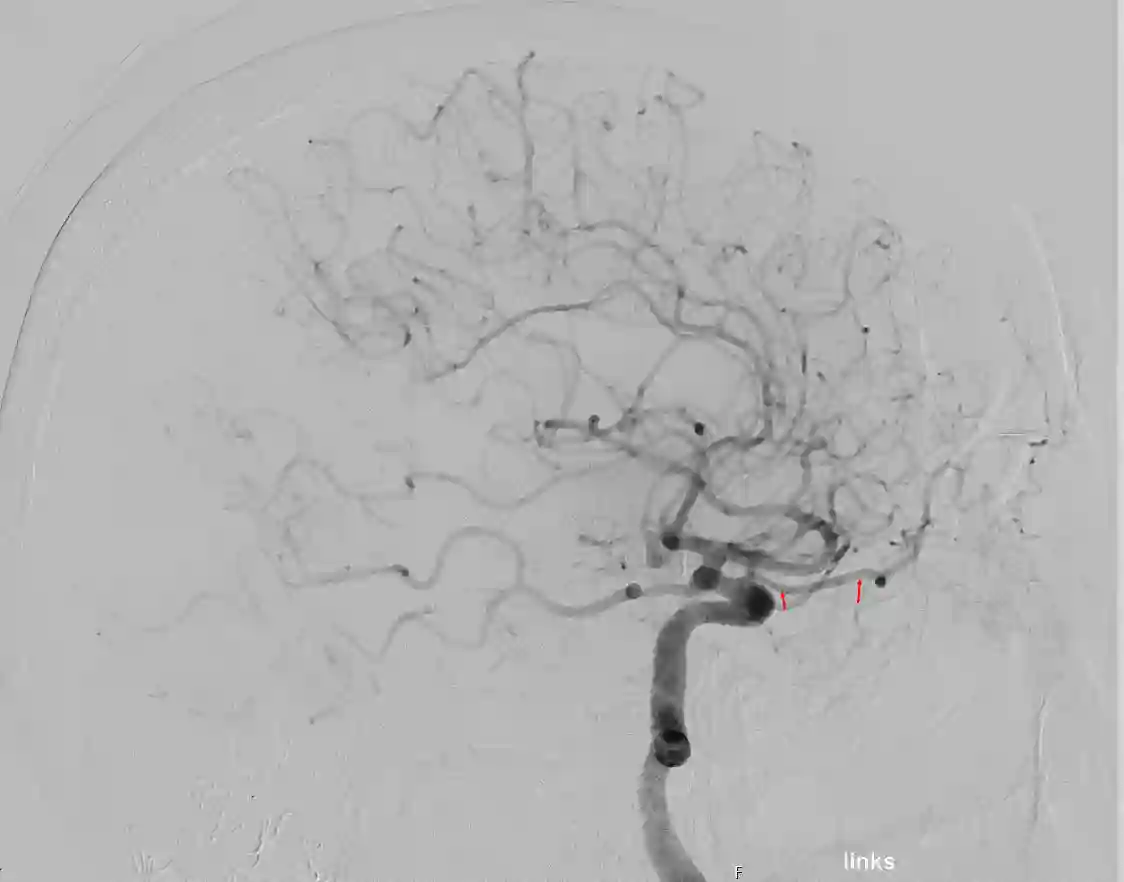
Imaging
The gold standard for the visualization of the ophthalmic artery is the digital subtraction angiography.
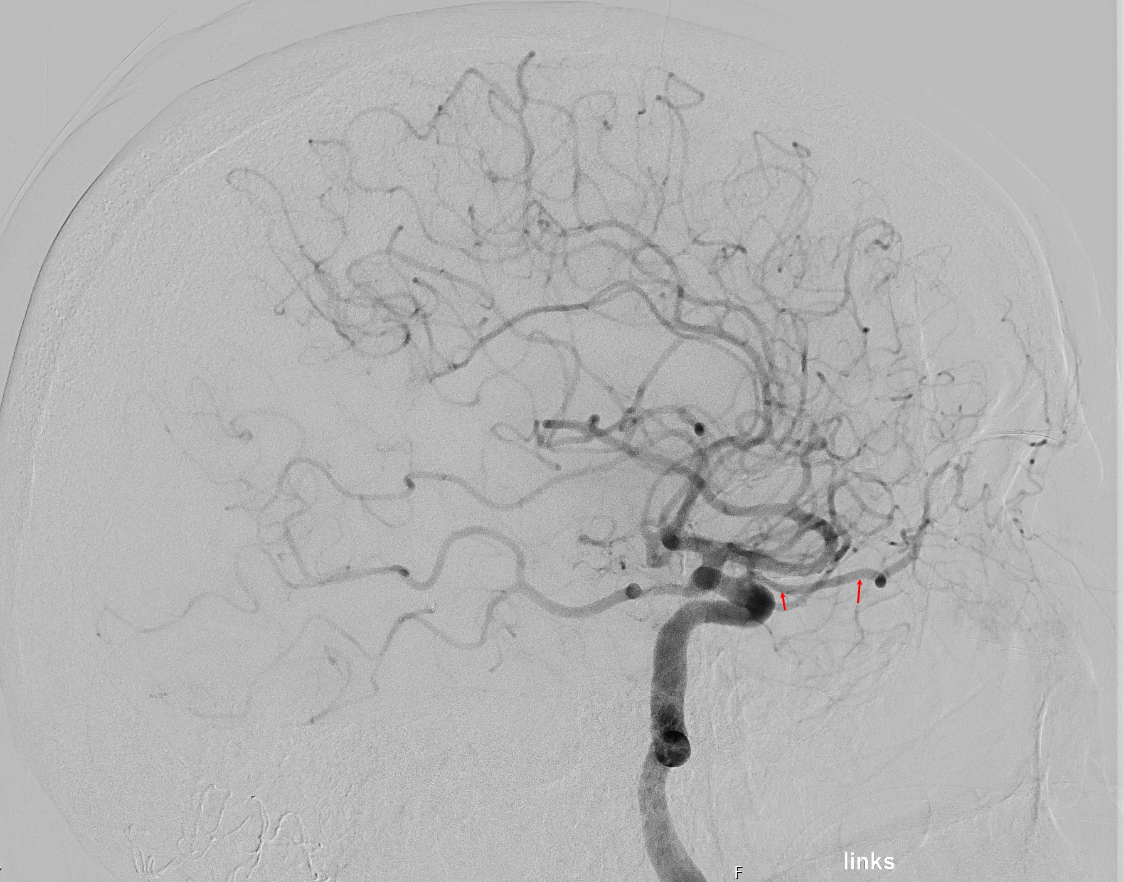
Symptoms
An occlusion of the ophthalmic artery results in monocular blindness or amaurosis fugax. Due to the extensive collateral circulation with the external carotid artery, symptoms are often only transient[^2].