Galassi Classification
Last edit by Alaric Steinmetz on
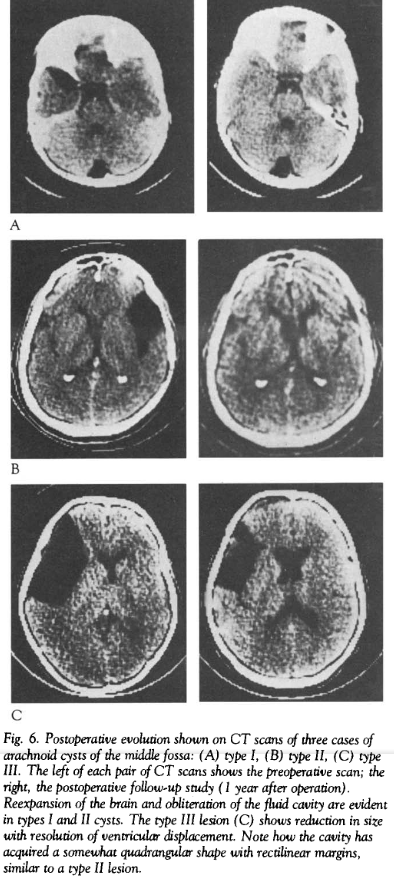
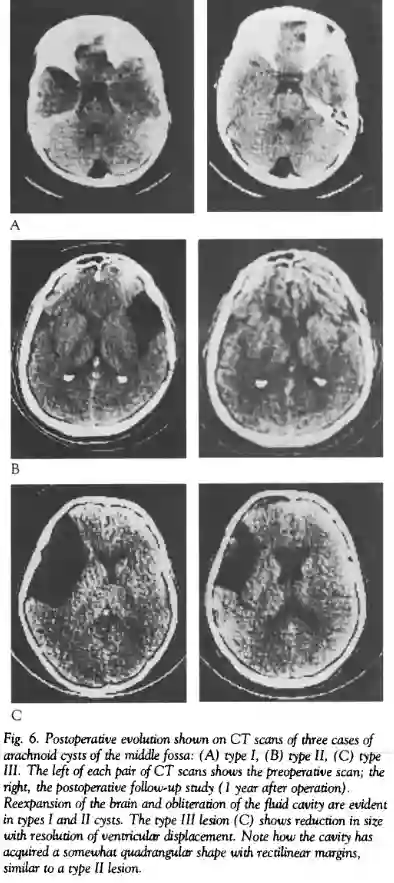
The Galassi classification is used in neuroradiology to categorize arachnoid cysts in the middle cranial fossa into three distinct types and was first described in 1982 by Galassi et al.[^1].
Classification
Galassi Type | Criteria |
Galassi Type I | Small, spindle-shaped. The cyst is located in the anterior part of the temporal fossa. The temporal pole is compressed posteriorly but does not have a significant space-occupying effect. There is no displacement of the ventricular system or midline. |
Galassi Type II | The lesion is medium-sized and in a triangular or quadrangular shape. The lesion occupies the anterior and middle part of the temporal fossa and extends superiorly along the Sylvian fissure. The temporal lobe appears shortened. |
Galassi Type III | The lesion is large and appears oval or round. It almost completely fills the space in the temporal fossa, extending into the respective hemisphere and separating the operculum from the Sylvian fissure. The temporal lobe appears atrophic, and the frontal and parietal lobes are largely compressed. There is a clear mass effect with a shift of the ventricular system and the midline. |
Figure